Table of Contents
Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea
To diagnose pediatric sleep apnea, the doctor will check your child’s symptoms and medical history and have a physical exam. They might order several tests to diagnose the condition. Tests might comprise of:
- Polysomnogram
Doctors check your child’s condition during an overnight sleep study. This test utilizes sensors applied to the body to keep a record of brain wave activity, breathing patterns, snoring, oxygen levels, heart rate, and muscle activity while your child is asleep.
- Oximetry
If doctors especially suspect obstructive sleep apnea and a complete polysomnogram isn’t needed or available, an overnight recording of oxygen levels might assist make the diagnosis.
- Electrocardiogram
In an electrocardiogram, sensors are patched with wires attached (electrodes). They measure the electrical impulses produced by your child’s heart. Doctors may use this test to know if your child has a hidden heart condition.
Treatment

Before and after tonsillectomy
Your doctor will collaborate with you to find the most effective treatment for your child’s sleep apnea. Treatment might comprise of:
- Removal of the tonsils and adenoids
Your doctor might recommend your child to a pediatric ear, nose, and throat specialist to discuss extracting the tonsils and adenoids. An adenotonsillectomy might improve obstructive sleep apnea by opening the airway.
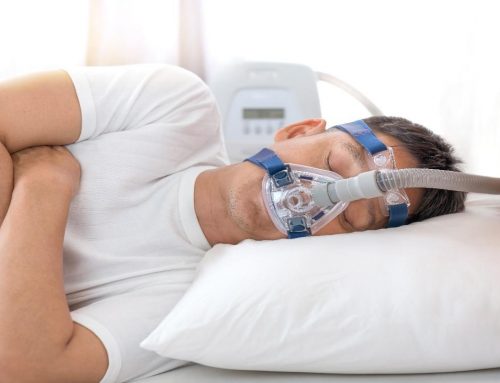
- Positive airway pressure therapy
In repetitive positive airway pressure (CPAP) and bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP), small machines lightly blow air through a tube and mask mounted to your child’s nose, or nose and mouth. The device supplies air pressure into the back of your child’s throat to keep your child’s airway open. Doctors often remedy pediatric obstructive sleep apnea with positive airway pressure therapy.
- Oral appliances
Oral appliances, including dental devices or mouthpieces, move your child’s bottom jaw and tongue ahead to keep your child’s upper airway open. Dental specialists have experience creating oral appliances to treat sleep apnea.
Lifestyle and home remedies

Proper dieting and weight loss management can reduce the effects of sleep apnea
- Avoid airway irritants and allergens
All children, but specifically those with pediatric obstructive sleep apnea, should shun tobacco smoke or other indoor allergens or pollutants, as they can create airway irritation and congestion.
- Weight loss
Doctors may suggest that your child lose weight if he or she is obese. Your doctor can give you and your child a diet and nutrition guideline, or refer your child to other specialists with specialization in managing obesity.



 Shop
Shop