Table of Contents
Causes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea

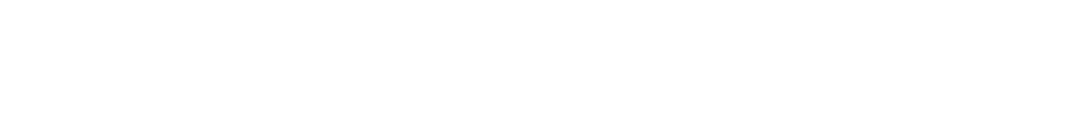
Obstructive sleep apnea is a common and dangerous disorder that causes intermittent breathing or holding breath while sleeping for 10 seconds or more. The disorder leads to decreased oxygen in the blood and can briefly awaken patients throughout the night.
There are various sleep apnea causes. The most common trigger of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in adults is excess weight and obesity. OSA is associated with the soft tissue of the mouth and throat. During sleep, this soft tissue can cause the airway to become blocked when the throat and tongue muscles are more relaxed. However, several other factors also are associated with the condition in adults.
In children, causes of obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea often comprise enlarged tonsils or adenoids. Dental conditions like a large overbite can also be attributable to these conditions in children. Less common causes include birth defects such as Down syndrome and Pierre-Robin syndrome and a tumor or growth in the airway.
Notably, down Syndrome causes enlargement of the tongue, adenoids, and tonsils. Consequently, there is a reduced muscle tone in the upper airway. On the other hand, Pierre-Robin syndrome develops a small lower jaw, and the tongue tends to ball up and fall towards the back of the throat. Even though childhood obesity may lead to obstructive sleep apnea, it is less commonly associated with the condition than adult obesity.
Regardless of age, failure to seek treatment of sleep apnea can lead to severe complications such as cardiovascular disease, accidents, and premature death. Therefore, it is essential that anyone with signs and symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea, receive an appropriate medical evaluation. Common symptoms include loud snoring and repeated nighttime awakenings, followed by excessive daytime sleepiness.
Other Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Other anatomical features related to obstructive sleep apnea include a narrow throat, thick neck, and round head. Many of these features are hereditary. Contributing factors may consist of hypothyroidism, excessive, and abnormal growth due to acromegaly – production of excessive growth hormone. Allergies and other medical conditions like a deviated septum that lead to congestion in the upper airways may also cause sleep apnea.
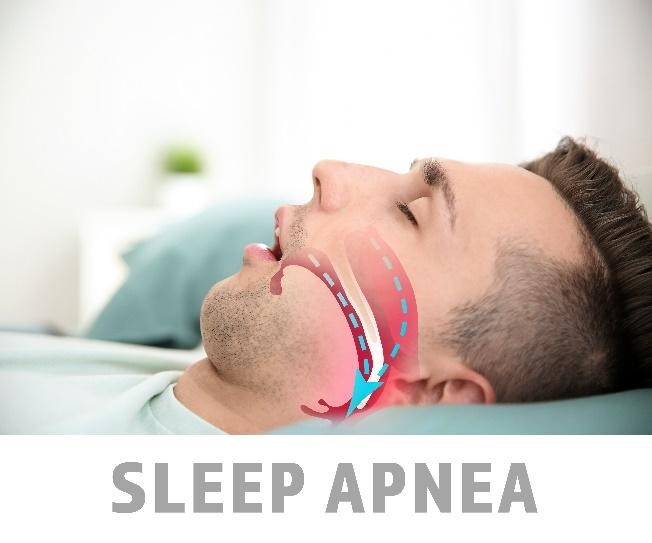
In adults, smoking, excessive alcohol use, and the use of sedatives can also cause obstructive sleep apnea. The benefits of treating sleep apnea may improve the signs and symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea and its complications. Medical treatment may include control of risk factors, use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or oral appliances, and surgery.




 Shop
Shop